It is believed that there is a huge black hole in the center of the galaxy. In this case, what will inevitably happen isWhich came first, the galaxy or the black hole?is the question. Until now, the accepted theory was that black holes are born after galaxies form.
However, a research team led by Joseph Selke of the Sorbonne University found that by combining observational data of the early universe from the James Webb Space Telescope with simulation results,Galaxies and black holes were born almost simultaneously, and black holes accelerated the process of star formation in galaxies.We have announced the results of our research. This result confirms the possibility of the existence of earlier galaxies than previously expected, as shown by Webb Space Telescope observations.
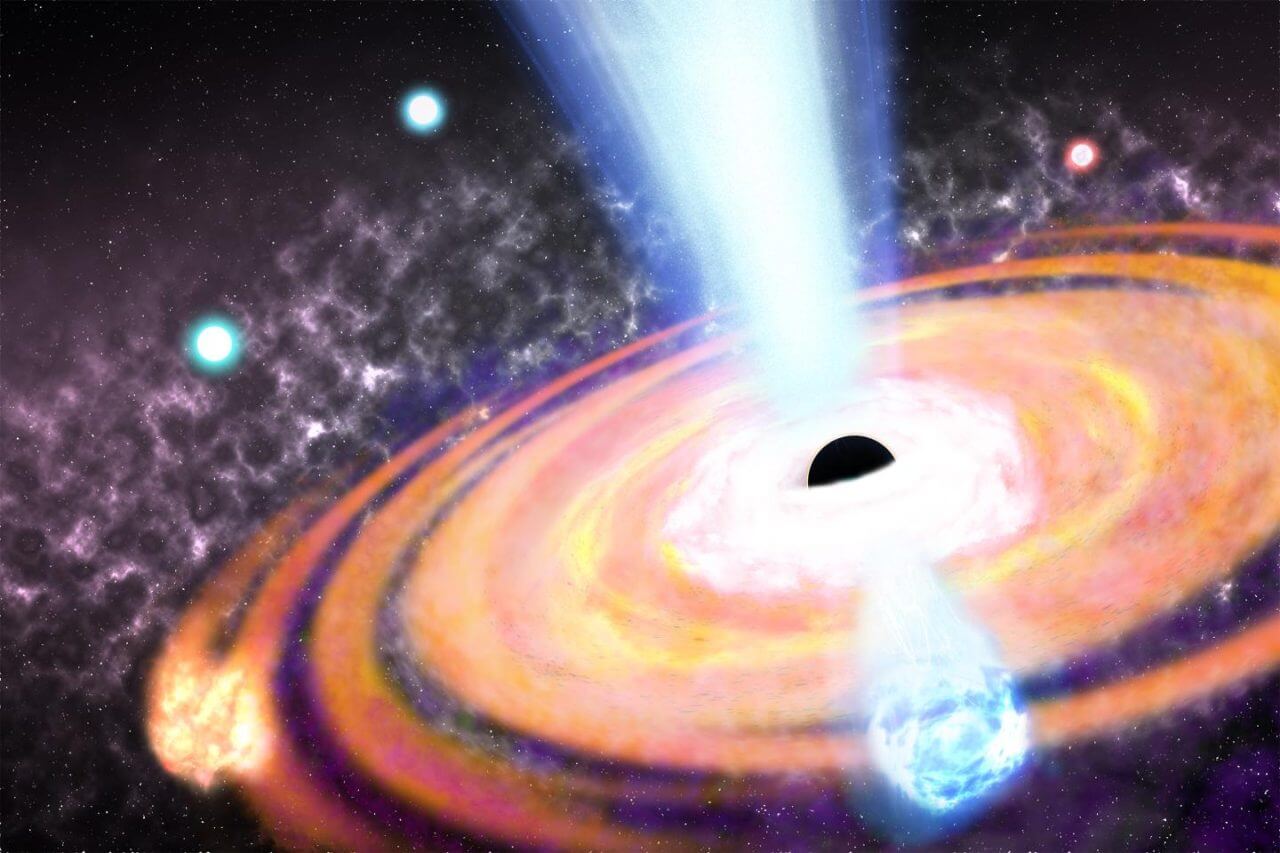

■ “What came first, the galaxy or the black hole?”
“Which came first, the chicken or the egg?” It is a well-known philosophical dilemma related to biology. There is a similar problem in astronomyWhich came first, the galaxy or the black hole?There is a dilemma. Many galaxies, including our own Milky Way, are thought to have massive black holes at their centers. So which came first, the galaxy or the black hole?
If the black hole had come first, its powerful gravity would have pulled matter around it, and galaxies would eventually have formed. On the other hand, if galaxies came first, black holes can be thought to have arisen as a result of the gravitational collapse of giant stars born within a collection of matter called galaxies. Both are plausible, which raises the question of order.
Until now, it was accepted that galaxies come first, and black holes come later.He was. This is because giant black holes, such as those found at the centers of galaxies, are thought to have originated from extremely massive stars that could only have formed in the early universe. Such a star would rapidly explode into a supernova, causing its core to collapse due to the force of its gravity, creating a black hole. This is because this black hole is believed to have evolved into the giant black hole it is today by attracting a large amount of matter around it.
Based on this idea, the “seeds” of a supermassive black hole cannot be planted without the birth of a giant star and its gravitational collapse. It is believed that stars are born from masses of gas. Until now, it was thought that galaxies were born before black holes, because the first form of galaxies was thought to be clumps of gas held together by mutual gravity.
■Did galaxies and black holes form at about the same time?
However, the Webb Space Telescope, which began observations in 2022, made a discovery that casts doubt on this established theory. The high-performance Webb Space Telescope has obtained a lot of observational data about the early universe that has been difficult to observe until now. Of particular note is the discovery of a large number of very bright galaxies in the early universe. The number was much higher than previously expected. Modern astronomy faces the question of why there were so many bright galaxies in the early universe.
To solve this puzzle, a research team led by Joseph Selke of the Sorbonne University combined observational data on galaxies in the early universe from the Webb Space Telescope with simulations of the behavior of matter in the early universe. We've looked into what was happening in the early universe. As a result, contrary to conventional wisdom,Not only did black holes and galaxies form at roughly the same time, but they also influenced each other's evolution.This was a surprising result. In other words, the answer to the first question is that galaxies and black holes exist at the same time.
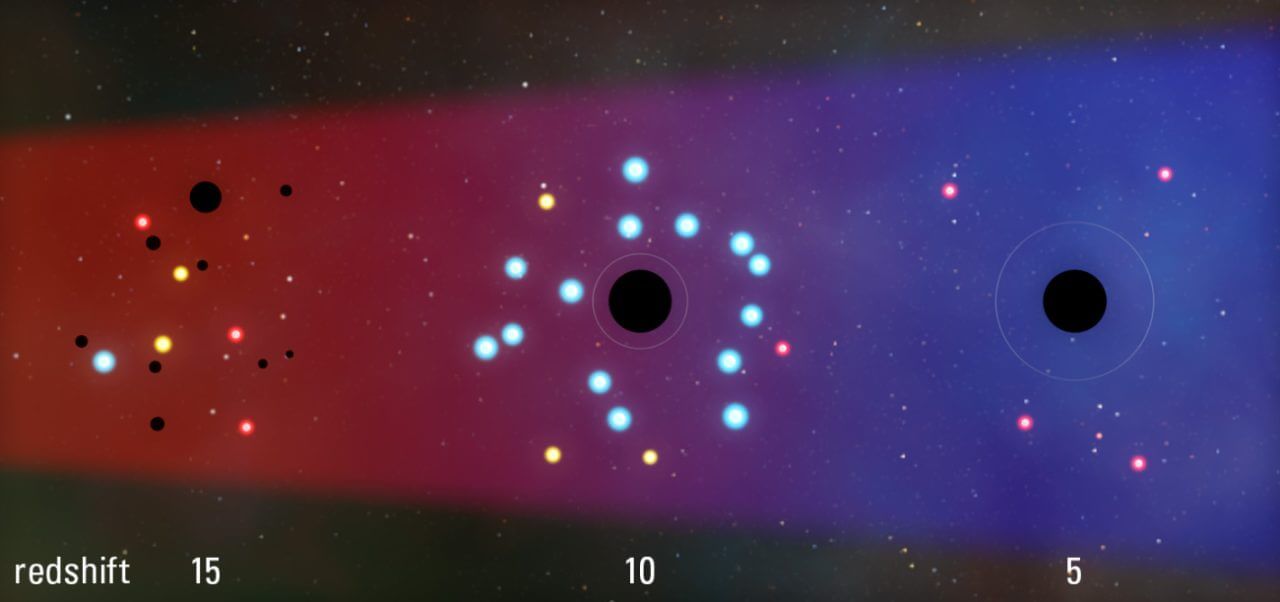

According to the research results of Silk et al., the co-evolution of galaxies and black holes in the early universe was as follows. First, in the very early stage of the universe's formation, about 300 million years after its birth, a huge gas cloud gathers, the center collapses to form a black hole, and the surrounding area forms stars. This is arguably the oldest form of galaxies.
The black hole then begins emitting intense, jet-like radiation by absorbing the gas surrounding it. This radiation displaces the surrounding gas clouds and increases their density, thus stars are actively born in regions of high density. At this stagePositive feedback from black hole activity that promotes star formationHe works. It is estimated that the era of positive feedback lasted from 300 to 1.2 billion years after the birth of the universe.
However, over time, the gas is gradually depleted as it is consumed by star formation or emitted from the galaxy by black holes. As the black hole's gravity continues to attract gas into its center, activity continues to be high, and as a result the loss of gas due to radiation advances, and the gas necessary for the birth of stars is also depleted. Unlike the previous stage, this stageNegative feedback that black hole activity prevents star formationIt can be said that it works. The era of negative feedback is believed to have begun 1.2 billion years after the birth of the universe.
■ How the Webb Space Telescope is changing the way we look at the early universe
While the current scenario presented by Silk and colleagues is very different from conventional theory, it fits well with observations made by the Webb Space Telescope. The early galaxies discovered by the Webb Space Telescope date back to 900 million years after the birth of the universe, and in Silk's scenario the era of positive feedback has ended and we are entering the era of negative feedback, which is consistent with the times.
In an era of positive feedback, the galaxy is covered by so much gas that the black hole's radiation is masked. On the other hand, during the era of negative feedback, the gas is depleted and the radiation becomes more noticeable. Telescopes from the era before the Webb Space Telescope could barely see galaxies in the era of positive feedback, so traditional theory relied on the brightness of galaxies observable in the era of negative feedback. So, to some extent, it is natural that if a galaxy in the era of positive feedback were observed by the Webb Space Telescope, the existing theory would be overturned.
Nowadays, observations of the early universe have only begun using the Webb Space Telescope, so it is difficult to verify Silk et al.'s scenario, which upends existing theory. Silk and his colleagues believe that more observational data will be collected over the next year or so, which will provide answers to many questions, including the validity of this scenario.
source
- Joseph Silk, et al. “Which Came First: Supermassive Black Holes or Galaxies? Insights from JWST.” (The Astrophysical Journal Letters)
- Kenna Hughes Castleberry. “New results from the James Webb Space Telescope: How black holes went from creating stars to extinguishing them”. (Joint Institute for Laboratory Astrophysics)
- Roberto Molar Candanosa. “Which came first: black holes or galaxies?” (Johns Hopkins University)
Written by Riri Aya

“Travel maven. Beer expert. Subtly charming alcohol fan. Internet junkie. Avid bacon scholar.”





More Stories
It's better to call it a digital camera. The Xperia 1 VI lets you take any kind of photo | Gizmodo Japan
Google may be developing a new device called “Google TV Streamer” to replace “Chromecast”
What do you want to talk about? “Persona 3 Reload” recommendation campaign is running until July 31st! |.Persona Channel