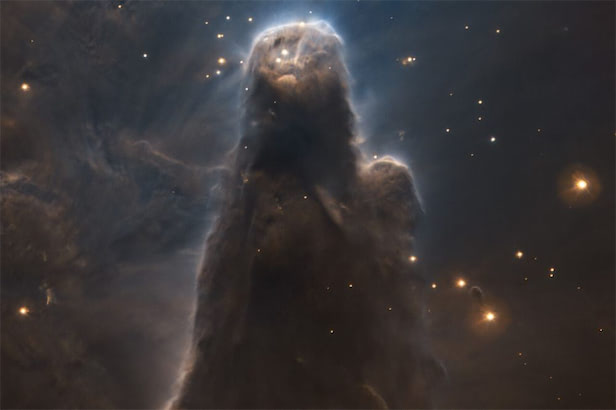
The European Southern Observatory (ESO) has released an all-new image of the famous Cone Nebula to mark its 60th anniversary. It looks like a creature from the depths of the sea.
An image of the nebula (the giant region where stars form) was taken by ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VTL) in Chile in 2022.
About 2,700 light-years from Earth, in the Orion Arm of the Milky Way (relatively close to our solar system on cosmic scales), the Cone Nebula is found in the constellation of the Unicorn. It is an ideal location for a distant object that has a horn-like shape.
The main feature of the nebula is the central column of gas and dust in which stars are still forming. The pillar, which appears to have one eye and one mouth, is seven light years long.
This Digital Sky Survey (DSS) image shows the region of sky around the Cone Nebula. The region of nebula in the center of the image, NGC 2264, contains the Christmas Tree Cluster and the Cone Nebula visible below (ESO/DIGITIZED SKY SURVEY 2. ACKN, https://www.eso.org/public/usa/images/eso2215c/?lang)
The conical nebula belongs to a star-forming region called NGC 2264. NGC 2264 was discovered by William Herschel, the German-born British astronomer in 1785 who discovered Uranus in 1781.
NGC 2264, also known as the “Christmas Tree Cluster,” is best seen in December from both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
Recently captured by the James Webb Space Telescope, “The Return”pillar of creationSimilarly, a giant cloud similar to the Cone Nebula of cool molecular gas and dust forms when blue stars emit strong stellar winds and ultraviolet rays that blast everything in the vicinity. This gas and dust is compressed to create a plume of darkness.
The new image was taken with the VLT’s Very Large Telescope, using a filter that makes hydrogen gas blue and sulfur gas red. Every telescope uses filters to bring out different wavelengths of light and different gases and other matter, but in this image the bright blue stars appear golden.
I wish clear skies and big eyes.

“Travel maven. Beer expert. Subtly charming alcohol fan. Internet junkie. Avid bacon scholar.”






More Stories
Global Gear launches new casual game “Psycho Boy 2”…the latest in the popular loose escape game series with a total of 120 million views on TikTok |
Voyager action in the 'Planetary' pavilion to celebrate 47 years of spacecraft's achievements World Premiere at Sumida in Tanabata: Tokyo Shimbun Tokyo Web
Rocks taken out from NASA's experiment to change the orbit of an asteroid may collide with Mars in the future. Space Portal website |