Project lecturer Kazuki Kato (Institute for Advanced Science and Technology Research, University of Tokyo) and colleagues conducted joint research with MIT, demonstrating that the Cas7-11-Csx29 complex, which is involved in the biological defense mechanism of prokaryotes, is activated by acid binding. target RNA, and we discovered that an RNA-dependent protein (protease) that cleaves the Csx30 protein. We also showed that the conformation of Csx29 protein changes upon binding to target RNA. It is expected to be applied to various technologies such as targeted RNA detection. The results are published online in the American journal Science on November 3.
Cas7-11, a prokaryotic type III-E CRISPR-Cas enzyme that degrades viral RNA and DNA, forming a complex with a short RNA fragment (guide RNA) that contains a sequence complementary to the target RNA , and acts as an RNA-dependent RNA cleavage enzyme (exonuclease) that cleaves target RNA based on(Fig. 1)。
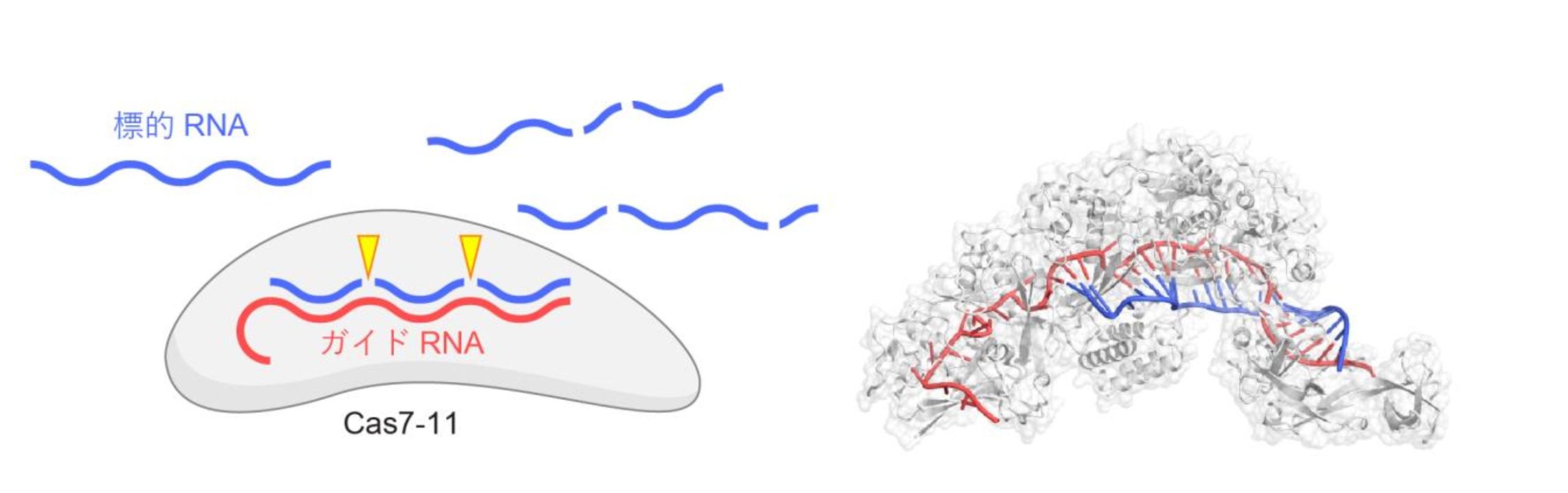
Type III-E CRISPR-Cas regions in prokaryotic genes produce five proteins, including Cas7-11, Csx29 and Csx30, which are proposed to be involved in antiviral defence. Csx29 has an amino acid sequence similar to known proteases and was known to form a complex with Cas7-11, but its function was unknown.
Research has found that Cas7-11 forms a complex with guide RNA and Csx29. We have shown that when a target RNA with a sequence complementary to the guide RNA binds to the complex, Csx29 is activated and cleaves Csx30 in two, restricting its function.

In addition, using cryo-electron microscopy, the 3D structures of the ‘Cas7-11 guide RNA-Csx29 complex’ and the ‘Cas7-11 RNA-Csx29 target RNA complex’ to which the target RNA binds are elucidated. These comparisons indicate that Csx29 undergoes conformational changes upon binding to its target RNA and has Csx30 cleaving activity, revealing the molecular mechanism by which the nucleic acid-dependent Cas7-11-Csx29 complex functions.

Using the fact that Csx29 cleaves Csx30 only when there is a target RNA complementary to the guide RNA, we also succeeded in detecting the presence of the target RNA as a fluorescence. The RNA-dependent enzyme with dual properties of endonuclease and protease is unprecedented and is expected to be applied to new technologies.
【Related Articles】
Connection

“Travel maven. Beer expert. Subtly charming alcohol fan. Internet junkie. Avid bacon scholar.”







More Stories
The ranking of the best survival horror games selected by the IGN US editorial team has been released! Resident Evil RE:2 ranked first
Enjoy a hot cigarette while looking at whales and tropical fish under the sea ⁉︎ “Ploom Dive” is an amazing spatial video experience using Apple Vision Pro
Apple Watch now supports sleep apnea, watchOS 11 released – Impress Watch