Watch the video below, created by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. This video compares the sizes of 10 supermassive black holes (supermassive black holes) and our solar system.
Supermassive black holes are celestial bodies that are said to be found in the center of various galaxies, and their mass ranges from hundreds of thousands to billions of times that of the Sun, and sometimes reaches more than 10 billion times.
[▲ مقارنة حجم 10 ثقوب سوداء فائقة الكتلة تم إنشاؤها بواسطة مركز جودارد لرحلات الفضاء التابع لناسا والنظام الشمسي]
(Credit: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Concept Image Lab)
The size of the black hole is compared based on the size of the black shadow that can be seen at the center. The shadows are caused by the black hole’s powerful gravity bending the direction of light around it. According to NASA, the diameter of the shadow is the “event horizon” (the maximum distance that light can escape from the black hole’s gravity). twice the size of the virtual ball drawn). The ring around the shadow represents the fall of hot gas as it orbits the black hole, and the color indicates the temperature of the gas (blue is higher than red).
[▲ من الفيديو: الشمس (وسط) والثقب الأسود الهائل للمجرة القزمة 1601 + 3113 (أسفل اليمين) (مصدر الصورة: مختبر الصور المفاهيمية التابع لمركز جودارد لرحلات الفضاء التابع لناسا)]
The first thing that appears in the video is our sun. The black hole of the dwarf galaxy “1601+3113” is visible in the lower right. The mass of this black hole is about 100,000 times that of the sun, and the size of the shadow is said to be smaller than the size of the sun. As the field of view expands, the black holes of spiral galaxy Circinus and elliptical galaxy M32 (Messier 32) appear.
![【▲ From the video: Supermassive black holes at the centers of the Compass Galaxy (left side of the Sun), M32 (same lower left), and the Milky Way (lower right). The circles show the orbits of Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars from the inside[Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab]](https://sorae.info/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/supermassive-black-hole-size-comparision-with-solar-system-2023-05-02-1.jpg)
【▲ From the video: Supermassive black holes at the centers of the Compass Galaxy (left side of the Sun), M32 (same lower left), and the Milky Way (lower right). The circles show the orbits of Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars from the inside[Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab]
The fourth to appear is the “Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*)” black hole at the center of the Milky Way. Sagittarius A* has a mass about 4.3 million times that of the Sun and the diameter of the shadow is half the diameter of Mercury’s orbit. In May 2022, the international research team “Event Horizon Telescope (EHT)” announced research results that captured Sagittarius A*’s shadow by radio waves, and it became a hot topic.
-B-
Related topics:[تعليق]Successful imaging of the supermassive black hole “Sagittarius A*” in the Milky Way! Her chart was captured (May 13, 2022)
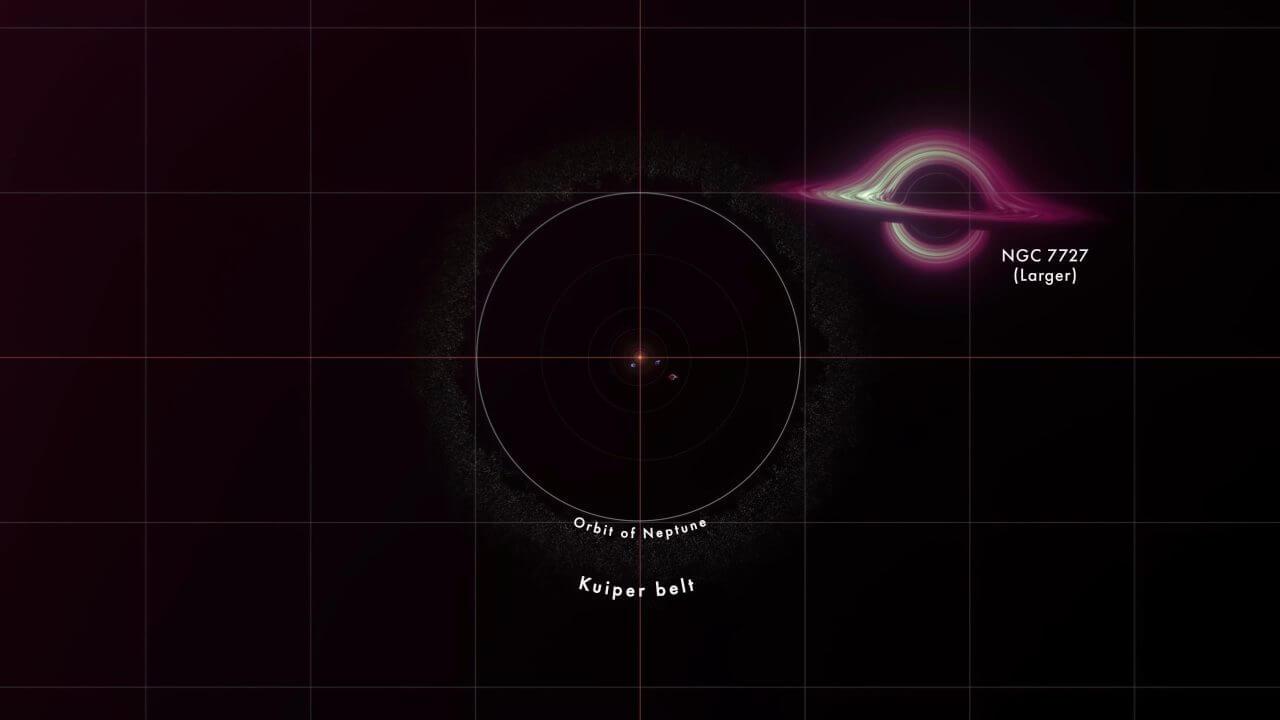
【▲ From the video: The most massive supermassive black hole at the center of the alien galaxy “NGC 7727” (top right). The circle indicates the orbit of Neptune (Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab)]
The next two black holes are located at the center of the strange galaxy “NGC 7727” and are said to be about 6 million times more massive and more than 150 million times that of the sun. The two black holes are only about 1,600 light-years apart, and they are expected to merge into a single black hole in about 250 million years from what they currently monitor.
Related: A pair of supermassive black holes discovered in a galaxy 89 million light-years from Earth (December 3, 2021)
At this point, the video already shows a range beyond Neptune’s orbit, and the nature of the size comparison between supermassive black holes becomes more apparent.
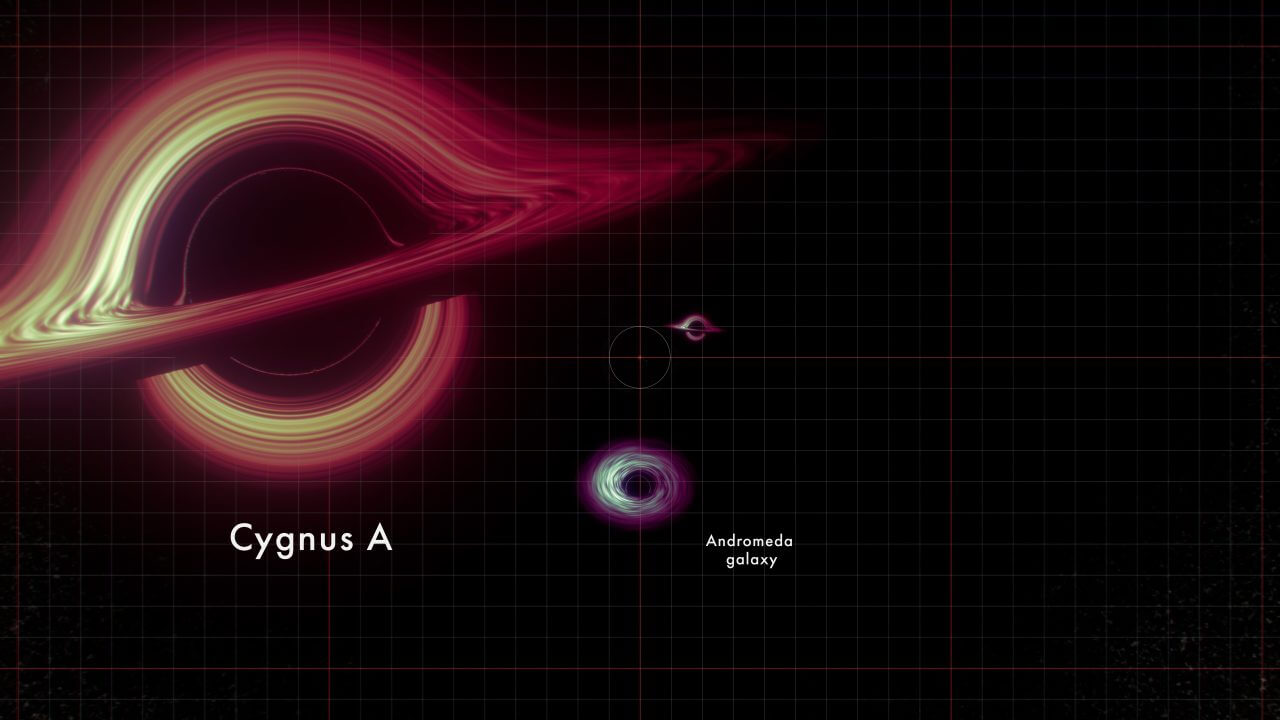
[▲ من الفيديو: الثقوب السوداء الهائلة في مركز المجرة الراديوية “Cygnus A” والمجرة الحلزونية “مجرة أندروميدا” (Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Centre Conceptual Image Lab)]
The seventh to appear is a black hole in the famous spiral galaxy “Andromeda Galaxy (M31)” near the Milky Way. Next to it, the black hole of the giant radio galaxy “Cygnus A” is visible. The mass of the black hole in Cygnus A is estimated to be about 2.5 billion times that of the Sun.
The black hole of the elliptical galaxy M87 (Messier 87) appears when the Oort Cloud, also known as the comet’s nest, begins to appear. NASA estimates that the supermassive black hole at M87’s center is about 5.4 billion times the mass of the Sun, based on the latest observations from the Hubble Space Telescope and the WM Keck Observatory in Hawaii. The diameter of the shadow is large compared to its mass, and it is said that it takes about two and a half days to cross it even at the speed of light.
![[▲ من الفيديو: ثقب أسود هائل في المجرة البيضاوية M87 (أسفل اليمين) (Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab)]](https://sorae.info/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/supermassive-black-hole-size-comparision-with-solar-system-2023-05-02-3.jpg)
[▲ من الفيديو: ثقب أسود هائل في المجرة البيضاوية M87 (أسفل اليمين) (Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab)]
In April 2019, the aforementioned EHT announced that it had successfully captured the shadow of this black hole for the first time ever. I think many people have seen the image as an orange colored ring, but I think we managed to capture the shadow of this black hole and the root jet emanating from the center of M87 at the same time. The results were only announced that day.
Related: For the first time, we have successfully captured the structure around a supermassive black hole and root jet simultaneously (April 27, 2023)
At the end of the video, the tenth is the black hole of quasar TON 618 (Tonantzintla 618), which is more than 10 billion light-years from Earth. A quasar is a type of active galactic nucleus (AGN) that emits powerful electromagnetic waves from a narrow region at the galactic center.
-B-

【▲ From the video: TON 618’s quasar supermassive black hole (left). The small object visible at the far right is the elliptical galaxy’s M87 supermassive black hole (Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab)]
According to NASA, the estimated mass of the black hole driving TON 618’s activity is about 60 billion times that of our Sun. It is said that the diameter of the shadow takes weeks to cross the speed of light.
Merging galaxies is not uncommon in the universe, galaxies have been observed in various stages of merging, and it is expected that the Milky Way galaxy and the Andromeda galaxy will merge into one galaxy within billions of years, here I am. As evidenced by the fifth and sixth black holes, NGC 7727, the supermassive black holes at the galactic center are also thought to have merged and grown during the repeated process of intergalactic mergers.
The video released this time is short, less than two minutes, but it makes you feel once again the scale of the vast universe and the long history.
* Distances are expressed in the article as “optical path distances” (light path distances), which refer to the distance that light emitted from a celestial body travels before it is observed on Earth.
source
- Image credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab
- NASA – NASA animation magnifies the size of the largest black holes in the universe
- NASA Science Visualization Studio – NASA animation magnifies the size of the largest black holes in the universe
Sentence editing section

“Travel maven. Beer expert. Subtly charming alcohol fan. Internet junkie. Avid bacon scholar.”






More Stories
Enjoy a hot cigarette while looking at whales and tropical fish under the sea ⁉︎ “Ploom Dive” is an amazing spatial video experience using Apple Vision Pro
Apple Watch now supports sleep apnea, watchOS 11 released – Impress Watch
ASCII.jp: New macOS Release! macOS Sequoia 15 Can Display Your iPhone Screen on Your Mac!