「Gamma ray burstIt is one of the most active phenomena in the universe, and one of the main mysteries is the mechanism by which long-duration gamma-ray bursts occur.
A research team led by Marcus DuPont and Andrew Macfadyen of New York University discovered through simulations that when a star collapses, a phenomenon occurs in which condensed plasma flows from the equator. ThisThe stream moves at speeds close to the speed of light, fast enough to tear apart a star.The author colloquially refers to this phenomenon as “Relative code(Relative cipher).”
■ Gamma-ray burst is a mysterious phenomenon
A “gamma-ray burst” is one of the most high-energy astronomical phenomena in the universe, emitting high-energy gamma rays in a short period of time, a phenomenon that occurs alongside a supernova explosion that occurs in a star much larger than the Sun and is believed to be the case. However, many mysteries remain regarding its mechanism of occurrence.
One of the big mysteries is why gamma-ray bursts release large amounts of energy in a limited area. The energy of the gamma ray burst is so great that it is believed that it can only be explained by considering that it was emitted in a small area. Therefore, a mechanism is needed to narrow the direction of energy release.
[▲الشكل 1: انطباع الفنان عن انفجار أشعة غاما (مصدر الصورة: NASA, Swift, Mary Pat Hrybyk-Keith, John Jones)]
The currently supported theory is that this is due to the formation of “magnetars” that occur in the cores of stars. When nuclear fusion stops in the nucleus, gravitational collapse occurs where the nucleus collapses due to gravity, creating an extremely dense, rapidly rotating magnetar. A magnetar has a very strong magnetic field that causes plasma, which are electrically charged particles, to move at high speed. The source of gamma-ray bursts is thought to be the release of energy resulting from plasma flows and collisions between star-forming particles.
In the current study, this mechanism explains the release of energy along the spin axis, which is a good explanation for short-lived gamma-ray bursts. However, although the number is small, gamma-ray bursts that shine longer have also been observed, and this mechanism has not been sufficient to explain them.
■ Discovering the “blade” that emanates from the center of the star
The DuPont and MacFadyen research team modeled the activity inside the star and simulated the flow of matter and energy. As a result, we discovered that a previously unknown flow of energy can occur.
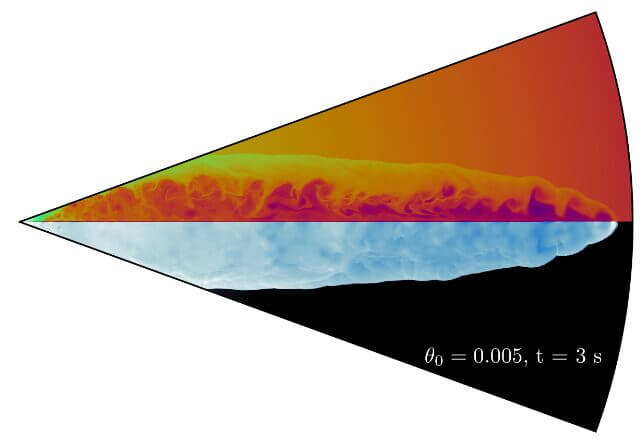
[▲الشكل 2: مثال لمحاكاة “الشفرة النسبية”. ومن المميزات أنها تحدث بشكل رقيق في اتجاه خط الاستواء (مصدر الصورة: DuPont & MacFadyen)]
If the magnetar’s rotation speed is too fast, the flow of particles will be concentrated toward the equator due to rapid changes in the magnetic field. A violent flow of plasma occurs towards the equator of the magnetar, that is, towards the equator of the star itself. Although the speed of the flowing plasma reaches almost the speed of light, its thickness is very thin compared to the size of the star, so the plasma can fly outside the star and reach a distance several times the radius, and in the process generates a large amount of energy, and it has been found that it emits Of which.
The research team called this plasma flow “sheet” or “blade” because it propagates in a plane, unlike a jet, which has a linear shape. Because of its speed, the research team called it the “relative code.” This is because the outward flow of plasma from the equator can be described as being sufficient to cut a star in two.
■Research is in its early stages
In situations where relativistic ciphers occur, their force is 50 times more powerful than a typical supernova explosion.(about 5 x 10 joules to the 45th power)Equivalent energy is releasedIt is considered. Researchers believe this may be the key to gamma-ray bursts, as the total energy and emission time are consistent with long-duration gamma-ray bursts.
This study only proves that the relativistic code is compatible with gamma-ray bursts, and the research is still in its early stages. As a next step, the research team plans to examine how the blade changes over time and how it affects the ultimate fate of the star.
source
Written by Riri Aya

“Travel maven. Beer expert. Subtly charming alcohol fan. Internet junkie. Avid bacon scholar.”






More Stories
The ranking of the best survival horror games selected by the IGN US editorial team has been released! Resident Evil RE:2 ranked first
Enjoy a hot cigarette while looking at whales and tropical fish under the sea ⁉︎ “Ploom Dive” is an amazing spatial video experience using Apple Vision Pro
Apple Watch now supports sleep apnea, watchOS 11 released – Impress Watch