technology
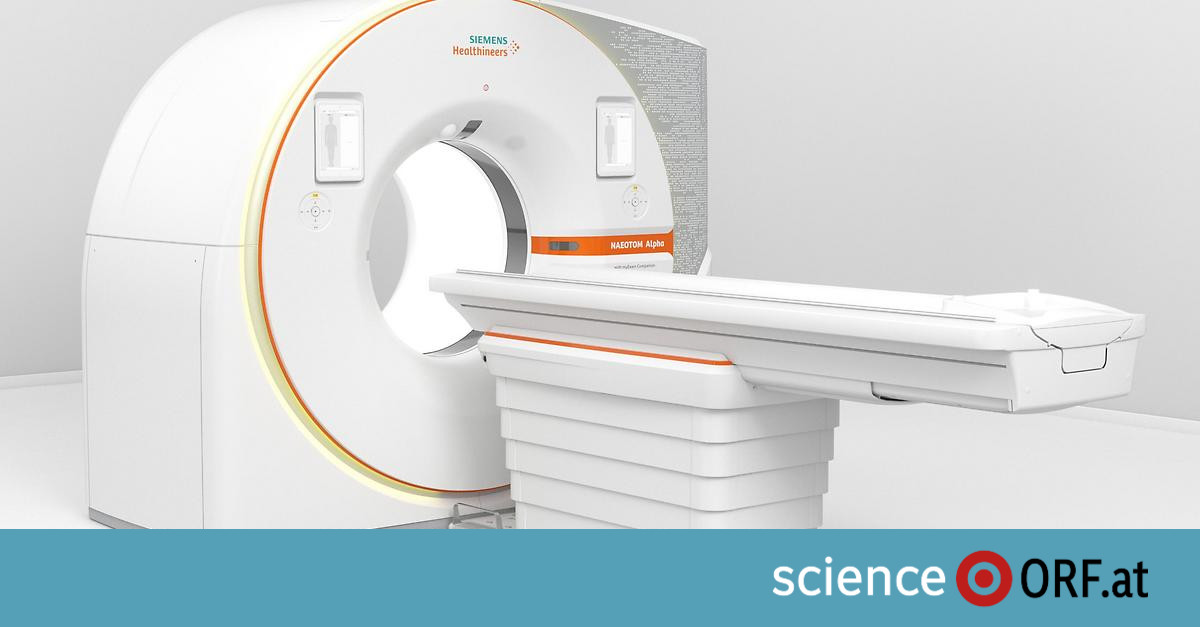
One of the world’s first high-resolution computer tomography (CT) scans was presented in Graz on Tuesday. The device can capture each X-ray photon and its energy level directly, rather than first converting it into visible light as in a classic CT scan.
This enables clearer, higher-contrast images, as was said in the presentation Diagnostic Center Graz.
Get more x-rays
Developed by Siemens Healthineers, a subsidiary of Siemens device It is one of about 25 photon counting devices worldwide and offers “a radical improvement to previously known imaging,” explains Peter Kolling, medical director of the Diagnostic Center in Graz. “Not only do the quantitative count scans generate more usable data, but it is also possible to scan the lungs on the move without the patient having to hold their breath,” continued the radiologist in Graz.
Conventional CT scanners convert X-rays into visible light, which is then converted into an electric current. The digital image is created with this energy. However, information is lost during the conversion of light into electricity: this results in reduced image contrast and reduced image sharpness. The new technology makes more use of X-rays.
Quantum counter
In the fall of 2021 Foot Siemens Healthineers has the first CT scanner certified for clinical use with the new technology, which is now also used in Graz: the system converts X-ray photons – that is, optical quanta – directly into electrical signals. The new X-ray detector is capable of calculating individual quantities in each pixel. Hence the name “quantum computed tomography”.
The higher spatial resolution of the new technology makes it possible to see anatomical structures that were not previously visible using conventional computed tomography – tumors are easier to identify as such. The new method also has advantages when it comes to imaging the anatomy of the lungs.

“Certified tv guru. Reader. Professional writer. Avid introvert. Extreme pop culture buff.”






More Stories
Samsung Quantum Dot TV: Art meets technology
Pitch: €56m for energy startup Reverion
Plastoplan: Plastics for Energy Transition