The current Earth rotates once every 24 hours, but it is believed that the Earth’s rotation period continues to slow down, and the Earth in the past was thought to rotate faster. increase. So far, the deceleration rate is assumed to be constant.
However, a research team led by Ross N. Mitchell of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Uwe Kircher of Eberhardt Kahl-University Tübingen found thatbillion yearsThere is almost no decrease in rotational speed,The day was roughly fixed at about 19 o’clockExplain it. This period isA billion years of boredom(Boring Billion)”, which is an interesting finding.
![[▲ الشكل 1: رسم تخطيطي مفاهيمي لعزم دوران المد والجزر. إذا كانت الفترة المدارية للكائن B (الرمادي) الذي يدور حول الكائن A (الأزرق) هي نفس فترة الدوران ، فإن المحور الرئيسي للكائن B يتم محاذاته مع الكائن A (الشكل الأيمن). ومع ذلك ، إذا لم تتطابق الفترة المدارية مع فترة الدوران ، فلن يصطفوا في خط مستقيم ، وستعمل القوة على استعادة الانحراف (الشكل الأيسر). تسمى الظاهرة التي تتغير فيها فترة دوران الجسم السماوي B بسبب هذا الإجراء عزم دوران المد والجزر. (مصدر الصورة: WikiMedia Commons / Matryosika)]](https://sorae.info/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Mid-Proterozoic_day_length-001.jpg)
[▲ الشكل 1: رسم تخطيطي مفاهيمي لعزم دوران المد والجزر. إذا كانت الفترة المدارية للكائن B (الرمادي) الذي يدور حول الكائن A (الأزرق) هي نفس فترة الدوران ، فإن المحور الرئيسي للكائن B يتم محاذاته مع الكائن A (الشكل الأيمن). ومع ذلك ، إذا لم تتطابق الفترة المدارية مع فترة الدوران ، فلن يصطفوا في خط مستقيم ، وستعمل القوة على استعادة الانحراف (الشكل الأيسر). تسمى الظاهرة التي تتغير فيها فترة دوران الجسم السماوي ب بسبب هذا الفعل عزم المد والجزر (Credit: WikiMedia Commons / Matryosika)]
Why is the Earth’s rotation period prolonged? It includes the Moon, the only satellite of the Earth. The Moon’s gravity pulls on the Earth, causing the Earth to elongate slightly, like a rugby ball. At this time, the stable arrangement is dynamic so that the long side vertices of the slightly deformed Earth are aligned with the Moon.
However, since the Earth’s rotational speed is about 30 times faster than the Moon’s orbital speed, the crest of the long side of the deformed Earth crosses the straight line connecting the Moon’s center of gravity with Earth. At this time, the Moon pulls the overpassed part and tries to bring it back to a straight line, so the Earth’s rotation is broken. This phenomenon is called “tidal moment”.
As it continues to be affected by the tidal torque, the Earth’s rotation speed gradually slows down, and the rotation period increases. Liquid seawater is more deformable than the solid crust and is more susceptible to tidal moment, so the tidal moment of the moon is “Ocean tidal momentIt is also called.
However, the Earth not only receives circumferential tidal momentum from the Moon, but also “Thermal tidal momentIt also works. The thermal tidal torque is caused by the expansion of the atmosphere due to the heating of water vapor and ozone in the atmosphere by the sun. Although its effect is very weak compared to the tidal torque in the ocean, it is noted that it is a torque that accelerates the speed of Earth’s rotation vs. Tidal moment in the ocean.
![[▲ الشكل 2: دوران الأرض يتباطأ تدريجياً بسبب عزم المد والجزر المحيطي الناجم عن جاذبية القمر. من ناحية أخرى ، فإن عزم المد والجزر الحراري الناجم عن حرارة الشمس يسرع من دوران الأرض. يُعتقد أنه كان هناك وقت في الماضي عندما كانت هذه الأمور متوازنة. (رصيد الصورة: Nature Geophysics / Mitchell & Kirscher)]](https://sorae.info/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Mid-Proterozoic_day_length-002.jpg)
[▲ الشكل 2: دوران الأرض يتباطأ تدريجياً بسبب عزم المد والجزر المحيطي الناجم عن جاذبية القمر. من ناحية أخرى ، فإن عزم المد والجزر الحراري الناجم عن حرارة الشمس يسرع من دوران الأرض. من المعتقد أنه كانت هناك فترة في الماضي كانت متوازنة فيها (Credit: Nature Geophysics / Mitchell & Kirscher)]
In the past, when the Earth was spinning faster than it is now, the tidal moment in the ocean is thought to have been much weaker, at one point less than a quarter of what it is today. During this period, the thermal tidal moment and the circumferential tidal moment were balanced, and the Earth’s rotational speed was a recession period in which no acceleration or deceleration occurred. The idea of a plateau in changes in the Earth’s rotation period has been proposed since about the 1980s, when it became possible to examine the geological and fossil records of antiquity in detail.
However, this idea remained a hypothesis for a long time. The main reason is the lack of geological records. Fossils such as corals and tree rings are useful for estimating how long a day on Earth was in the past, but these large organisms date back to the Eon of Life, beginning 540 million years ago. It did not appear until then, nor did it exist in the pre-Cambrian period.
Stromatolites are used
To estimate the period of Earth’s rotation in the age older than the eon of life, but only stratolites that meet certain conditions can be used for analysis. They are rarely found. In addition, it is very difficult to interpret the necessary conditions for the analysis, and it is not uncommon for different researchers to obtain completely different results even when analyzing the same sample. So it was a very difficult question to answer about the length of the day on Precambrian Earth.
* A rock with alternating layers of photosynthetic bacteria like cyanobacteria and grains like clay. Because the layers grow during the night, when photosynthesis is not occurring, the seasonal changes that occur during the day can be used to estimate the length of Earth’s past days. It is necessary to clear many strict conditions, such as the need to prove thatThe Mitchell and Kircher research team said,Milankovitch cycle
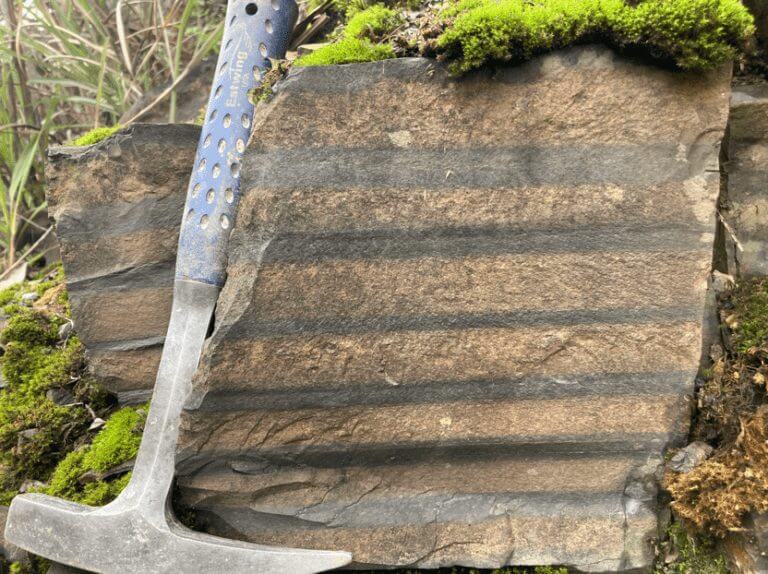

[▲ الشكل 3: أمثلة على الرواسب التي تم تحليلها. يعكس النمط المخطط ارتفاع مستوى سطح البحر ، ويمكن استخدام تحليله لتقدير فترة دوران الأرض. (رصيد الصورة: روس إن ميتشل)]
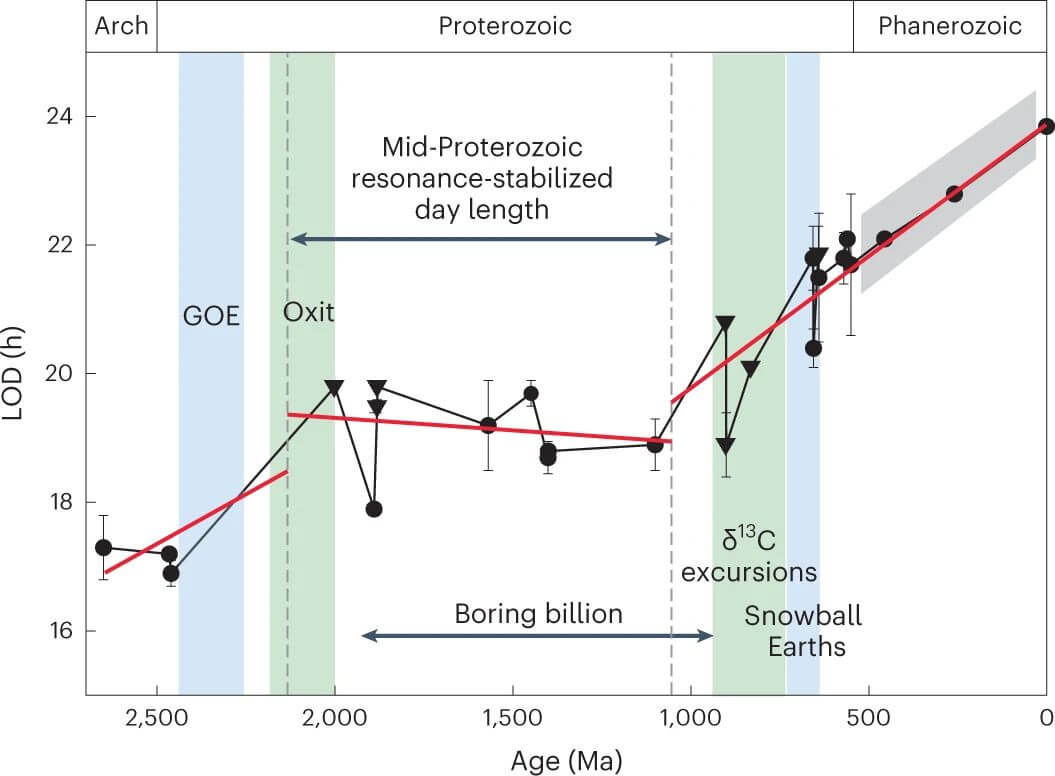
[▲ شكل 4: التغيرات في فترة دوران الأرض المقدرة في هذه الدراسة (الخط الأحمر). يمكن ملاحظة أن التغيير في فترة دوران الأرض ظل دون تغيير تقريبًا لمدة مليار سنة من حوالي 2 مليار سنة مضت إلى حوالي مليار سنة ماضية. أيضًا ، كانت بداية ونهاية فترة الهضبة أحداثًا لإمداد الأكسجين بكميات كبيرة. (رصيد الصورة: Nature Geophysics / Mitchell & Kirscher)]
Therefore, the research team analyzed the data of 22 layers from 2.65 billion years ago to 550 million years ago and examined changes in the Earth’s previous rotation period. As a result, it became clear that about a billion years ago, from about 2 billion years ago to about a billion years ago, the Earth’s rotation period hardly changed, and the day was approximately constant at about 19 hours. The analyzed data indicate that at some point between about 2.46 billion and about 2 billion years ago, tidal equilibrium and convective tidal moment and circulation slowdown stopped.
The period when the period of rotation hardly changed is an interesting period in Earth’s history. During the billion years from 1.8 billion years ago to 800 million years ago, when the rotation period was found to be nearly constant in this research, the crust and climate changed hardly, and the evolution of organisms was very rapid. It corresponds to a period called “a dull billion years” that was slow. The reason for the boring billion-year occurrence has been a long-standing mystery, but one hypothesis has been that there was no small change in the tidal force of the moon, which is the driving force for the motions of the earth’s crust. If the movement of the earth’s crust is rare, then the likelihood of climate change due to volcanic activity will decrease, and the supply of inorganic substances (the so-called minerals) that provide nutrients for living organisms will be scarce.
It is also known that the beginning and end of a boring billion years each had an event in which large amounts of free oxygen (O2) were available. The extent to which large fluctuations in oxygen supplies affected the beginning and end of the tedious billion years is still debated, but the study suggests that they may have at least affected the period of Earth’s rotation. Free oxygen forms ozone under the action of ultraviolet radiation, and ozone absorbs heat more effectively than water vapor. Thus, an increase in free oxygen may lead to an increase in the thermal tidal moment.
On the other hand, at the beginning of the boring billion years, the order of oxygen concentration increased and then decreased, while at the end the order changed from decreasing to increasing oxygen concentration. It is possible that this difference is related to the change in the rotational period, but this is not clear.
It’s unclear how accurately this study describes Earth’s history, but it may help us better understand the tedious billions of years, arguably characterized by an absence of features.
source
Text: Rare Aya

“Travel maven. Beer expert. Subtly charming alcohol fan. Internet junkie. Avid bacon scholar.”






More Stories
It's better to call it a digital camera. The Xperia 1 VI lets you take any kind of photo | Gizmodo Japan
Google may be developing a new device called “Google TV Streamer” to replace “Chromecast”
What do you want to talk about? “Persona 3 Reload” recommendation campaign is running until July 31st! |.Persona Channel