The “space station”, which provides a long-term living environment in outer space, has the potential to become an important relay station for extraterrestrial exploration and development. One of the options under consideration as a construction site for the space station is the countless “asteroids” in the solar system. However, building a massive space station on an asteroid that can artificially generate gravity by centrifugal force due to rotation is thought to be a story in the distant future due to the huge amount of resources required.
However, David W. Jensen, a former Technology Fellow at Rockwell Collins, has presented a method for building a rotating asteroid station that can be built with current levels of technology and relatively cheap money, and posted a preliminary version on arXiv. Accordingly,The construction period for the station body is at least 12 years, and the construction cost can reach $4.1 billion (about 600 billion yen).displayed. Although additional costs are required to build a habitable environment, it has been shown that it can be built sufficiently even at the current technological level.
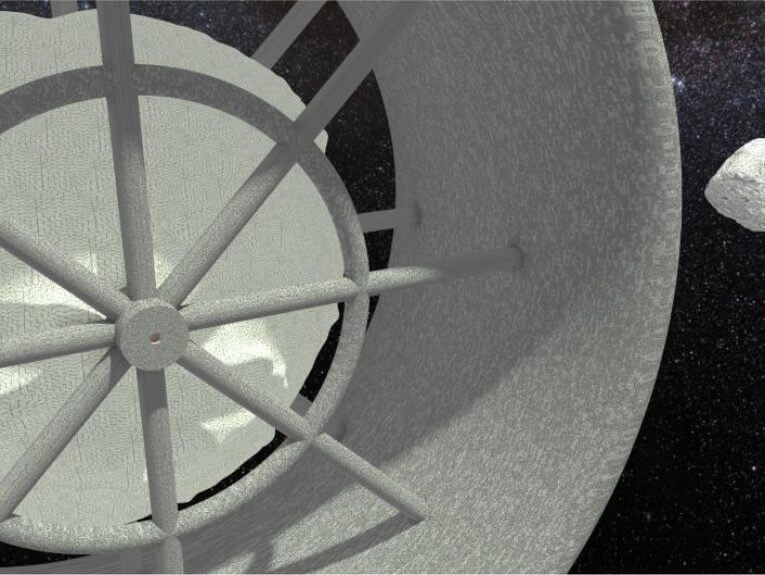
▲ Figure 1: Image of a circular-shaped space station centered around an asteroid (Photo credit: David W. Jensen)】
Asteroids are promising places to build a space station
The word “space station” is probably associated with structures in outer space, such as the International Space Station (ISS). Alternatively, one could envision structures built on the surface of relatively large celestial bodies, such as the currently considered lunar base, or even massive structures such as orbital elevators.
However, there are countlessasteroidIt has also been drawn to attention as a place to build a space station. Asteroids are so small compared to Earth and the Moon that their gravitational pull is almost negligible. Many asteroids come very close to Earth and have lower relative velocities, requiring less propellants (fuel and oxidizer) to reach them. It is also possible to use the asteroid itself as a raw material to make building materials for the station, so the amount of materials supplied from Earth will be minimal. In addition, there are advantages that are difficult to achieve with other types of stations, such as obtaining rotational force from the rotation of the asteroid to create artificial centrifugal gravity.
However, since it is expected that a large amount of resources will be required for construction, there has not been much interest as to whether they can actually be built, so until now building a space station on an asteroid was almost science fiction. has been considered. However, Jensen’s research shows that even with the current level of technology, this is not a difficult goal to achieve.
■ View the best asteroids and station construction methods
Jensen, who has proposed several asteroids, such as Ryugu and Bennu, as candidates for the construction site, said the best candidate is Asteroid 163693.Atera‘ Proposal. Attila is an asteroid about 4.8 km in diameter and a satellite about 1 km in diameter. Since they orbit roughly the same as Earth, they are expected to be useful in maintaining the station’s internal temperature.
![[▲ الشكل 2: الهيكل الداخلي لمحطة الحيد. ومن خلال جعل الجزء السفلي عبارة عن هيكل متعدد الطبقات، يتم زيادة المساحة الصالحة للسكن. (رصيد الصورة: ديفيد دبليو جنسن)]](https://sorae.info/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/2023-08-24-Atira_station-002.jpg)
[▲ الشكل 2: الهيكل الداخلي لمحطة الحيد. يزيد الهيكل السفلي متعدد الطبقات من المساحة الصالحة للسكن (مصدر الصورة: David W. Jensen)]
Subsequently, Mr. Jensen proposed a structure for the whole station, with a circular (in the shape of a donut) residential area centered on Attila, and connecting Attila and residential area with several columns. The wheel shape and spokes of this bike adopt a layered structure to increase the living quarters space, protect the interior from threats such as micrometeorites and radiation, and create artificial gravity through the centrifugal force of rotation. It is the form we have arrived at as a result of considering it easy to use when Attila’s rotational speed, however, must be adjusted to produce a suitable artificial gravity.
How can manpower be secured to build such a station? Mr. JensenSelf-replicating spider robots take over the construction rolesI suppose. Using Atera’s resources, the spider robot is expected to create advanced items such as anhydrous glass, which is the building material of the station itself, rock crushers, solar panels, and self-replicators. It is assumed that it is necessary to pre-prepare the parts only with the latest technology such as electronic equipment which cannot be created immediately and other additional supplies are not necessary.
■ Construction costs are high but not unrealistic
So what are the costs involved in doing these things? Jensen calculated the weight of the “seed” capsule for the first station to be sent to Attila at about 8.6 tons. The capsule will contain four spider robots, a simple base, and the 3,000 electronic devices necessary for the spider robots to self-replicate.
This “seed” isIt is the weight that can be loaded on the “Falcon Heavy” rocket, which is currently being run by SpaceX.There is only one, and in theory there is no need for additional supplies other than the “seed”. Jensen estimates that the minimum time required to build the station body on the asteroid is 12 years. However, this is the period needed to build the main body, and does not include the provision of essential supplies for human survival such as oxygen and water.
Jensen also pointed out that thisThe total cost of the asteroid station construction project is $4.1 billion (about 600 billion yen).I figured it out. It sounds like a ridiculously high cost, but given that the total cost of the Apollo program was $93 billion (about 13.5 trillion yen), it couldn’t be said to be that expensive. Similar sums include the amount paid by the Tokyo metropolitan government for the 2020 Tokyo Olympics (about 630 billion yen) and the cost of building the Large Hadron Collider (about 500 billion yen).
A total of 1 billion square meters of nothing (about the same size as Sapporo and Hiroshima),Only $4.1 per square metreJensen believes that the cost of building this asteroid station would be a realistic investment for some billionaires, since new habitats can be created at a cost of $1.
It is not yet known whether Jensen’s asteroid station building plan is really viable, and if so, how closely it will be identical to the original design. However, the initial version presented this time is interesting because it shows that building a massive station that seems to appear in science fiction is achievable even at the current technological level.
source
- David W Jensen. “Restructuring Independent Asteroids into Rotating Space Stations”. Favorite
- Andy Tomaswick. “New paper shows how to change an asteroid into a space habitat – in just 12 years”. (the universe today)
Text: Riri Aye

“Travel maven. Beer expert. Subtly charming alcohol fan. Internet junkie. Avid bacon scholar.”






More Stories
Enjoy a hot cigarette while looking at whales and tropical fish under the sea ⁉︎ “Ploom Dive” is an amazing spatial video experience using Apple Vision Pro
Apple Watch now supports sleep apnea, watchOS 11 released – Impress Watch
ASCII.jp: New macOS Release! macOS Sequoia 15 Can Display Your iPhone Screen on Your Mac!