Phaethon, the celestial body that is the source of the Geminid meteor showerIt has attracted attention because it is believed to be an asteroid with quite unusual properties. On the other hand, no meteorite classified as having properties similar to Phaethon has yet been identified, which has caused slow progress in research.
A research team led by Eric McLennan and Mikael Granvik from the University of Helsinki has discovered an unusual classification among meteorites:CY Chondrite(Yamato-type carbonaceous chondrite)” has properties similar to Phaeton. Whether this result is correct or not will be determined in 2028.(*as of writing time)The research team believes that monitoring Phaethon by the Japanese experimental deep space exploration vehicle DESTINY+ will be able to verify this relatively quickly.
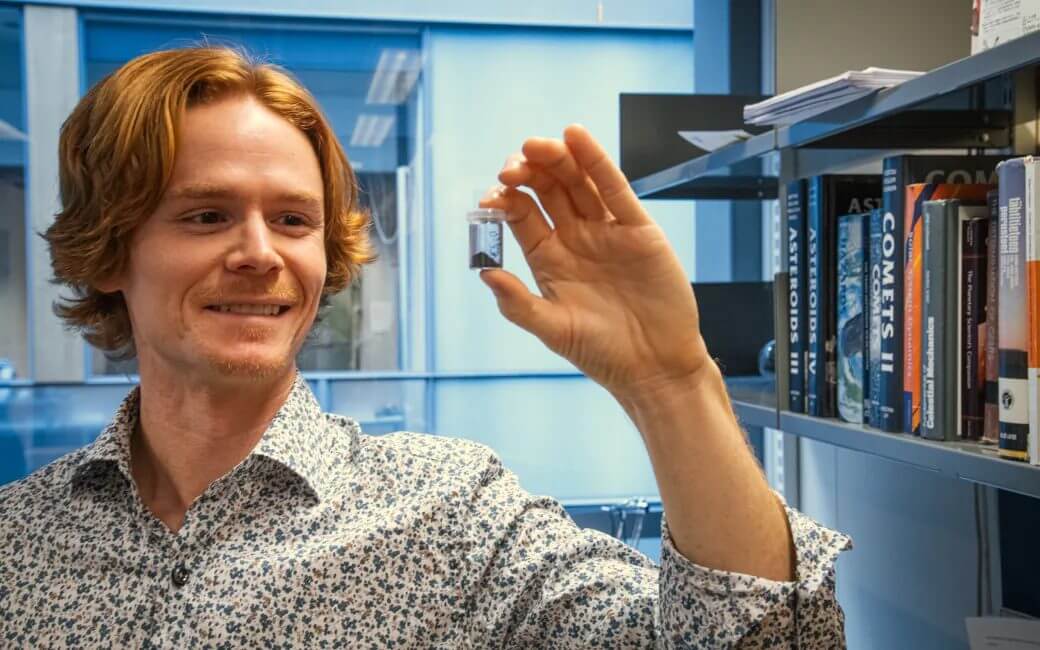
[▲الشكل 1: إريك ماكلينان يحمل عينة من كوندريت CY، والتي تم تحديدها في هذه الدراسة لتكون مشابهة لـ Phaethon (مصدر الصورة: سوزان هيكينن (جامعة هلسنكي))]
■ What meteor resembles Phaethon, the source of the Geminid meteor shower?
It is observed in mid-December every year.Geminid meteor shower“It is a meteor shower known alongside the Quadriids and Perseids. Meteor showers are believed to be a phenomenon that occurs when dust emitted from the surface of an active celestial body such as a comet enters the atmosphere. In the case of the Geminid meteor shower, the original body is the source of the dust(※1)Asteroid number 3200Phaethon“It is believed to be.
*1: A celestial body is the source of a specific celestial body. This is the celestial body that became the source of the meteorite.
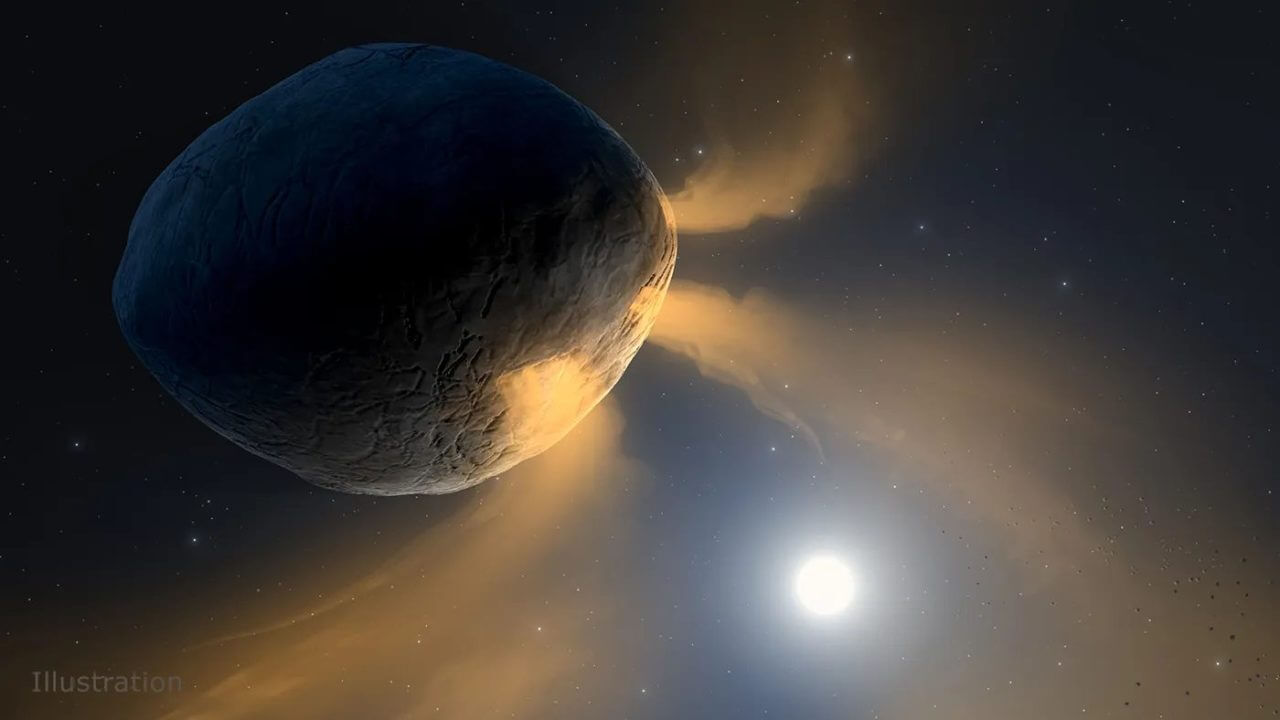

[▲الشكل 2: انطباع فني عن الغبار والغاز الذي ينبعث من فايثون (مصدر الصورة: NASA, JPL-Caltech & IPAC)]
Phaethon’s comet-like activity is so weak that it was initially thought to represent the “end of a comet” whose volatile components had been exhausted. However, recent research has begun to suggest that Phaethon was an asteroid from the beginning, and that its orbit that brings it so close to the sun causes it to spew out comet-like dust. In this case, the decomposition of rocks in Phaethon due to extremely high temperatures may be responsible for producing the dust.
Related article: Why did the ordinary asteroid “Phaethon” turn into an unusual comet? The original body of the Geminid meteor shower (May 10, 2023)
When testing hypotheses about an asteroid’s environment, analyzing meteorites with properties similar to those of an asteroid allows for more detailed research without the need for expensive and time-consuming re-sampling. However, in the case of Phaethon, no similar meteorite had been found yet, and there was a lack of evidence to solve the mystery.
■It turns out that Phaethon resembles the rare meteorite “CY chondrite”!
A research team led by McLennan and Granvik from the University of Helsinki examined previous observational data to identify meteorites similar to Phaethon. In this study, we examined mid-infrared monitoring data for Phaethon from NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope to see what kind of minerals Phaethon’s surface is composed of.
As a result of postulating several types of minerals and examining mineralogical compositions that closely match observational data, we found that the surface of Phaethon contains magnesium silicate (magnesium olivine), iron sulphide (truilite), and calcium hydroxide (borlite). Calcium carbonate (calcite), iron oxide (magnetite), and magnesium hydroxide (hydralite) have been identified. Given that the surface of Phaethon is heated to a maximum of about 800°C, these minerals are thought to have been produced by pyrolysis.
The research team believes that the composition and proportion of these minerals existCY Chondrite“It has proven to be a good match. This is the class to which only a small proportion of carbon-rich meteorites (carbonaceous chondrites) found in Antarctica belong, with only six having been found so far. (※2) . Most of the minerals in Phaethon and CY chondrites match each other.
*2…The CY chondrite classification is a new classification for carbonaceous chondrites that was proposed in 2018, but so far has only been used in academic research such as this one, and is not officially recognized by the International Meteorological Society. Registered as a classification.
There was a discrepancy in that magnesium oxide and calcium oxide, found in CY chondrite, were not found in Phaeton, and conversely, magnesium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide, found in Phaeton, were not found in CY chondrite. The research team believes this can be explained by the difference in environment between the large Phaethon and the small meteorite, as it is thought to have occurred due to whether water was involved during thermal decomposition.
The pyrolysis of metals that takes place at Phaethon also produces carbon dioxide, water vapor and sulfur gases. The research team suspected that these gases were the source of the dust, and conducted thermal modeling to simulate the state of the Phaeton’s surface. They found that the gases produced during pyrolysis generate enough pressure to break the surface of the rock into small pieces. There is a theory that the source of the dust on Phaethon is a giant collision in the past, but in the case of this research, it is also possible that dust on Phaethon is generated all the time.
Related article: Could Phaethon dust have been violently ejected by a previous celestial collision? Source of the Geminid meteor shower (June 30, 2023)
■Can you use “DESTINY+” to check if they are really similar?
If this theory that Phaethon resembles a CY chondrite is true, we will be able to learn more about Phaethon by examining in detail the Yamato 82162 meteorite, which is classified as a CY chondrite. However, it is currently unknown whether this theory is correct.
The research team is looking forward to the observation results of the deep space exploration experimental vehicle “DESTINY+” launched by JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency). DESTINY+ plans to conduct close observations of Phaethon in 2028(*as of writing time)Therefore, it will be possible to obtain more detailed observational data from Spitzer data. If this happens, it should become clear whether Phaethon really resembles a CY chondrite.
source
Written by Riri Aya

“Travel maven. Beer expert. Subtly charming alcohol fan. Internet junkie. Avid bacon scholar.”






More Stories
OPPO smartphone with Android 14 operating system. “Functional differences” occur in some models – OPPO Lab
The brightest gamma-ray burst in history turned out to be an ordinary supernova
Will it be the final display Qidi Vida |