Three of the visible planets would make interesting targets for skywatching tonight (June 30), though one of them will require staying up late.
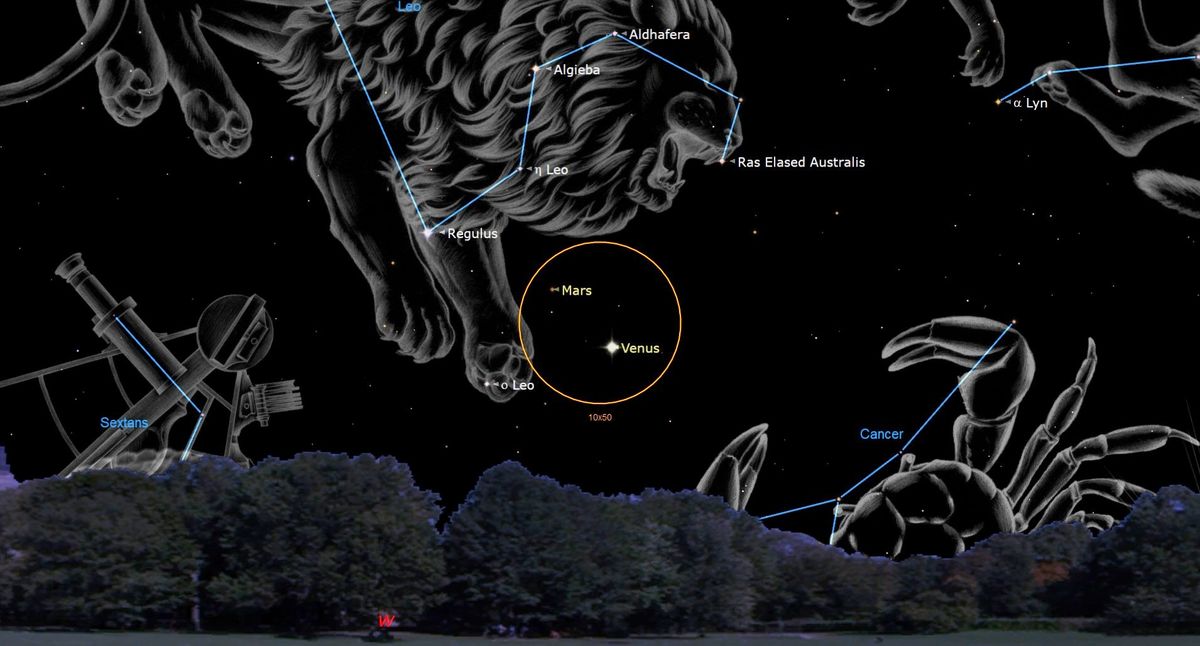
Mars and Venus will come very close in the night sky tonight and will be visible as the sun sets. Look west when it gets dark and find the pair below the Leo constellation, Leo. They will only be separated by 3 degrees, or about a third of the width of your hand held at arm’s length. The pair will set about 2.5 hours after sunset, disappearing around 11 PM EDT (0300 GMT Saturday, July 1).
Meanwhile, trickier Neptune will rise on the horizon to the east just after midnight Saturday. Its appearance marks the beginning of what is known as retrograde motion, meaning that the planet will begin to move westward through the constellations instead of in its regular eastward motion.
Related: Night sky, June 2023: What you can see tonight [maps]
Mars and Venus should be fairly easy to locate; Venus is still very bright in the night sky during what are known as its evening apparitions, which means that it appears at night. The planet is approaching its brightest star, which should happen on July 7 when it reaches magnitude -4.7 (the lower the magnitude, the brighter the object). By the end of July, the flower will set earlier and earlier so it starts to appear in the morning by mid-August.
Mars will be somewhat dimmer, though its proximity to bright Venus should help skywatchers find it. Look for a fixed (not twinkling) reddish orb above and to the left of Venus, the Evening Star.
The moon will be fairly bright tonight at 92% illuminated as it approaches the full moon phase on July 3. But it will start around 3 a.m. EDT (0700 GMT) on July 1, just in time for the attempt to locate Neptune.
Skywatchers interested in seeing Neptune enter retrograde motion will have to stay up late, as the planet won’t appear and begin to rise above the horizon until the early morning hours on Saturday. If you haven’t noticed Neptune before, just note that due to it being the farthest planet in our solar system, the ice giant appears very small and can be faint. Neptune will appear above the constellation of Cetus, Pisces, although if you are not familiar with locating it, it may be easiest to use a stargazing app on your computer or mobile device.
phenomenon retrograde motion It occurs due to the fact that the earth revolves around the sun; As our position in the solar system changes, so does our perspective when viewing distant objects like Neptune.
If you want to get a closer look at the planets of the night sky, our guides to the best telescopes and the best binoculars are a great place to start.
And for tips on photographing the night sky in general, check out our guide on how to photograph the moon and our lists on the best cameras for astrophotography and the best lenses for astrophotography.
Editor’s note: If you took a photo of Venus, Mars, or Neptune and would like to share it with Space.com readers, send your photo(s), comments, name, and location to [email protected].

“Extreme travel lover. Bacon fanatic. Troublemaker. Introvert. Passionate music fanatic.”






More Stories
A fossilized creature may explain a puzzling drawing on a rock wall.
MrBeast Sued Over ‘Unsafe Environment’ on Upcoming Amazon Reality Show | US TV
Watch comets Lemmon and SWAN approach Earth today