Expect a major source of microwave heating efficiency.
NASANASA's Artemis program aims to establish a lunar base as part of its human lunar exploration initiative. However, public expectations of this space base may differ from those depicted in popular science fiction films. Building a lunar base requires a wide range of building materials, which entail significant transportation costs. These materials must be launched from Earth using rockets.
Since transporting building materials from Earth to the Moon is expensive and time-consuming, local materials must be used to build a lunar base. One promising method for building a lunar base using local materials is microwave annealing, which hardens lunar soil (soil) below its melting point.
Active research on lunar soil sintering using lasers, solar energy and microwaves is currently underway around the world. Among these techniques, microwave sintering is a prominent technology being developed by various institutions, including NASA and the European Space Agency (European Space Agency), and the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Construction Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-suk).
Research in microwave sintering
A research team (Dr. Gangwon, Lee, Dr. Young-jae, Kim, and Dr. Hyun-woo, Jin) led by Dr. Hyo-sung, Shin at the Future and Smart Building Research Division of Korea Institute of Technology is currently conducting a study on microwave-molded lunar soil-simulating bricks. This research uses sintering techniques similar to ceramic firing, raising the temperature to create solid bricks.
Bricks made of lunar regolith simulants have a strength of more than 20 MPa, which is comparable to concrete. Microwave heating depends on the insulating properties of the material, so a detailed study of the insulating properties of lunar regolith is necessary. Currently, there is insufficient research on how lunar regolith reacts to microwave heating at different temperatures.
Investigation of lunar materials
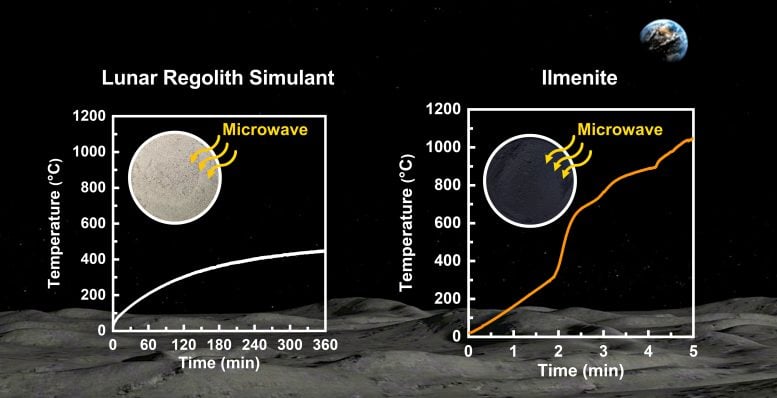
As part of the microwave sintering research, the research team investigated the dielectric properties of the Korean Lunar Simulant (KLS-1) and ilmenite (iron titanate) at different temperatures. Ilmenite is an abundant mineral on the Moon and is known to enhance the efficiency of microwave heating. However, detailed studies on the dielectric properties of ilmenite and its behavior during microwave heating have not been conducted.
The research results indicate that the lunar regolith simulation has the property of being transparent to microwaves, which makes it difficult to heat. However, ilmenite (iron titanate) interacts strongly with microwaves due to its unique crystal structure, which allows for rapid heating to high temperatures. In addition, the analysis of the crystal structures of the lunar regolith simulation and ilmenite successfully revealed the main factors contributing to the increased interactions of minerals with microwaves.
Using a domestic resource, ilmenite, as a heating element in the construction of the lunar base using microwave sintering means efficient and rapid production of building materials. Dr. Young-Jae Kim of the Korea Institute of Technology expressed his expectation that this research will be a crucial foundation for the development of microwave technology for future lunar exploration and lunar base construction.
Reference: “Temperature-dependent dielectric properties of Korean lunar ilmenite and ilmenite: potential for lunar microwave processing” by Young-Jae Kim, Hyun-Woo Jin, Jang-Gwon Lee, Byung-Hyun Ryu, Heo-Sung Shin, May 13, 2024, Building and construction materials.
DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.136599
This study was conducted under the KICT research program (Project No. 20230081-001, Development of Environmental Simulator and Advanced Construction Technologies on TRL6 in Extreme Conditions; Project No. 20230144-001, Space Architecture: Development of Basic Technology for Building Habitat on the Moon) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.

“Extreme travel lover. Bacon fanatic. Troublemaker. Introvert. Passionate music fanatic.”







More Stories
A review of Rhengling at Erfurt Theater
MrBeast Sued Over 'Unsafe Environment' on Upcoming Amazon Reality Show | US TV
A fossilized creature may explain a puzzling drawing on a rock wall.