A joint research group composed of Professor Hideji Fujii from the Department of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering, Osaka Institute of Technology (Chair: Susumu Inoue), and Associate Professor Apichat Imim, Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University (Chair: Bundhit Eua-arporn, Thailand) , has researched the creation of naturally derived polymer molecules, and has successfully developed liquid marbles that act as sensors to detect food spoilage.
[النقاط الرئيسية في هذه القضية]●Synthesize naturally derived molecules that repel water from polymers found in crabs, shrimp and ingredients found in coconuts.●Liquid marble, whose surface is covered in naturally derived molecules, acts as a sensor to detect food spoilage.
●The advanced food spoilage detection sensor can be easily produced and is safe even when in contact with food.
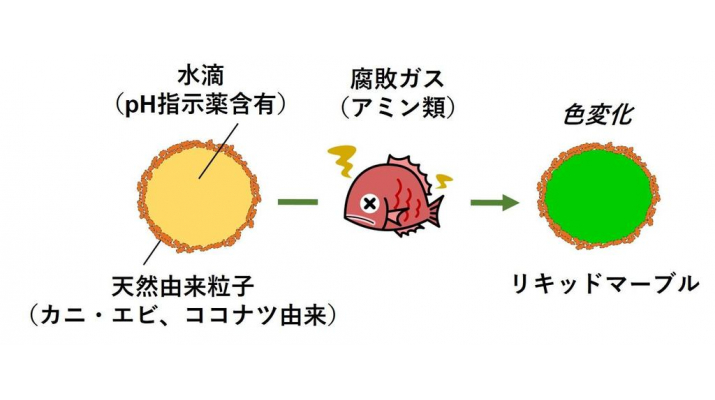
The issue of food loss caused by throwing away expired foods has become a hot topic. If we could find out if meat, fish, etc. are actually spoiled, it would be possible to reduce food loss. When food spoils, amino compounds such as ammonia are released as spoilage gases, so food spoilage detection sensors have been developed to detect these gases. However, conventional sensors face problems such as the need for expensive equipment and the difficulty of detection in microscopic spaces.
In this research, liquid marble (about 2 mm in diameter), whose surface is covered with naturally derived particles manufactured by combining a polymer (chitosan) found in crab and shrimp with a component found in coconut (stearic acid), is used as a food product material. We succeeded in using it as an accurate sensor to detect mold. The reagent, which changes color when it comes into contact with foul gas, dissolves in the water droplets inside it. It is easy to manufacture and can be rolled or slid into small spaces. It is able to easily detect food spoilage by visually monitoring color changes.
This result was obtained with support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Grant for Scientific Research (B), and the paper was published in the American Chemical Society academic journal ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering (February 27, 2024). ). )it has been. It was also selected as complementary cover art.
URL: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acssuschemeng.3c07724
(DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.3c07724)
▼ Contact information for this matter
Public Relations Office of the Joshu Gakuen Educational Foundation
Ichimura, Ueda
Address: 5-16-1 Omiya, Asahi-ku, Osaka
Tel: 06-6954-4026
Email: [email protected]

“Travel maven. Beer expert. Subtly charming alcohol fan. Internet junkie. Avid bacon scholar.”





More Stories
CGWORLD Volume 313 Pre-Announcement (September 2024 Release), “Let's Jump into VRChat Special Edition!”
It's better to call it a digital camera. The Xperia 1 VI lets you take any kind of photo | Gizmodo Japan
Google may be developing a new device called “Google TV Streamer” to replace “Chromecast”